"Point" based Image Processing Alogrithms
We discuss some of the Simplest image processing aglorithms. These include: thresholding, conversion, contrast stretching, threshold equalization, inversion, subtraction, averaging, grey level slicing, and bitplane slicing.
What all of these processes have in common is that they can be thought of as "Point Processes", meaning that they algorithm operates on one point or pixel at a time. Consider the case of producing a binary image from a greyscale image using thresholding. This is accomplished by comparing each pixel value with the threshold and consequently changing the pixel value.
One way that we can write "Point Processes is in terms of thier transformation function, T() as follows:
Pnew[r,c] = T(P[r,c])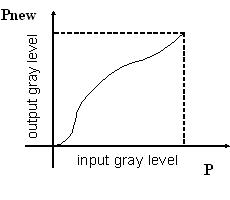
Where r= row, c= column (indicating the pixel location) and P[r,c] is the original image's pixel value at r,c. Pnew[] is the new pixel value. For each of the algorithms discussed, there will be a different transformation function.
Thresholding
 |
 |
for(r=0; r<M; r++)
for(c=0; c<N; c++)
{
if(P[r,c] < Threshold)
Pnew[r,c] = 0;
else
Pnew[r,c] = 255;
}
Conversion 
 |
 |
for(r=0; r<M; r++)
for(c=0; c<N; c++)
{
Pnew[r,c] = (Red[r,c] + Green[r,c] + Blue[r,c])/3;
}
Contrast Stretching
 |
 |
 |
 |
Inversion
 |
 |
for(r=0; r<M; r++)
for(c=0; c<N; c++)
{
Pnew[r,c] = 255 - P[r,c];
}
What would the transformation function look like? It is a straight line at
45 degrees. T(in)
255|
|\
| \
| \
| \
0| \
|_______\____
0 255 in
Grey Level Slicing 
This is an effect that can be used to highlight a
portion of the greyscale range. Consider a greyscale image of some coins. There
are coins made of silver and pennies made of copper. If you wanted to sort out
the pennies they would correspond to the darker grey circular objects in the
image. Hence you could highlight them in the image by mapping the midlevel grey
values to white and the rest to black. Below is what the transformation function
would look like for this case: T(in)
255| ___
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
0| | |
|__|_|_______
0 255 in
What would the algorithm be to implement the above transformation?
BitPlane Slicing 
 |
 |
Example:
If you had a greyscale image, meaning 8 bits are used to represent each pixel, and you sliced off the highest bit the following would be the Transformation produced. How could you implement this in C/C++? (Tip: there is a more efficient way than testing the greylevel value against thresholds.... hint think about masking the value).
T(in)
255|
|
|
| / /
| / | / |
| / | / |
|/___|/___|__
0 128 255 in
Image Subtraction 
Image Subtraction is the pixel-by-pixel subtraction of
one image from another. One use of Image Subtraction is the removal of the
background. Consider the application of detecting people that come up to an ATM
machine's camera. If you had a picture of the stationary background, and
subtracted it from a current image, then only the new items in the scene for
example a person, would be visible. The algorithm is shown below where I1 and I2
represent the two images. for(r=0; r<M; r++)
for(c=0; c<N; c++)
{
Pnew[r,c] = I1[r,c] - I2[r,c];
}
 Subtract green background to get only duck (Green screen technology)
Subtract green background to get only duck (Green screen technology) Image Averaging 
Image Averaging is the pixel-by-pixel averaving of two images. One use of Image
Averaging is the reduction of noise in the scene. Below is the algorithm where
I1 and I2 are the two images. Ofcourse more than two images can be averaged together.
for(r=0; r<M; r++)
for(c=0; c<N; c++)
{
Pnew[r,c] = (I1[r,c] + I2[r,c])/2;
}
 Add to duck picture (after subtracted green background)
Add to duck picture (after subtracted green background)
an image of a person in black.
Example showing use of some of the operations listed above
---security: where is the GUN?
NOTE: IR = infrared image
MMW = milimeter wave image
| IR image | MMW image | IR image morphologically filtered 5x5 | MMW image morphologically filtered 5x5 | IR filtered image thresholded | MMW filtered image thresholded |
IR and MMW images fused |
IR and MMW filtered images fused |
||||