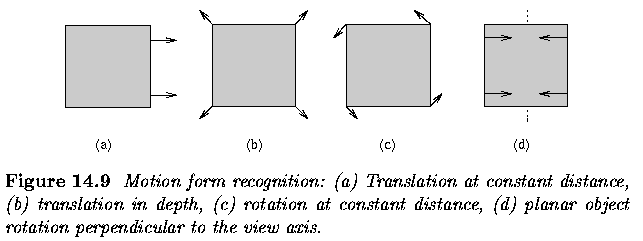
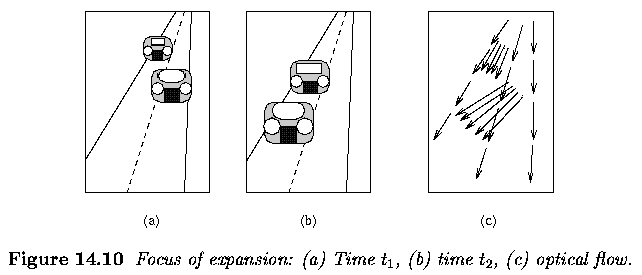
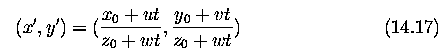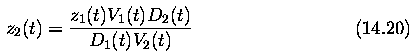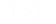Motion- Optical Flow
(parts adapted from http://www.icaen.uiowa.edu)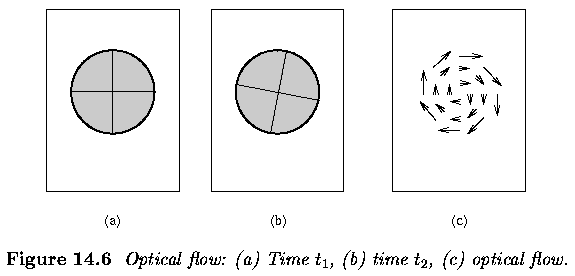
Optical Flow is an approximation of the 2D motion field. Motion in the world usually occurs in 3D, but, we have a 2D image sensor. So, we see the results as movement accross the 2D image plane. Hence we are seing the projection of the 3D moving points onto the image plane.
- Optical Flow Vector - describes motion of each point
- vector - image velocity of a point in the image
What can we do with this?
- Motion Detection
- Motion Compensation
- Motion-based Data Compression
- 3D scene reconstruction
- Autonomous Navigation
Can we really do all of this given we have only the projection of the 3D movement?
- Well...not really....we need to make some assumptions to accomplish the above, especially when reasoning about 3D (either reconstruction or motion).
- For example, one assumption often made is
the changes in image intensities in the image are caused only by motion.
when will this not be true (....illumination sources moving, objects entering/exiting the scene, occlusions)
Optical flow computation
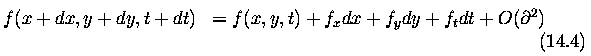
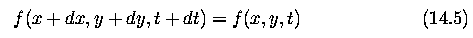

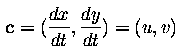
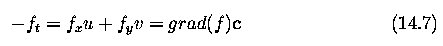
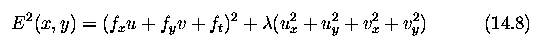
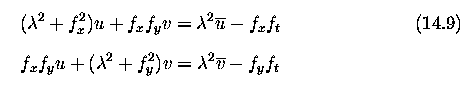


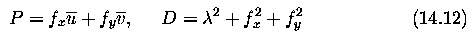



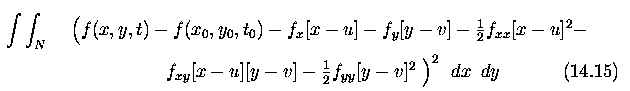
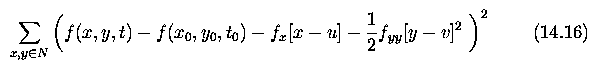
Global and local optical flow estimation
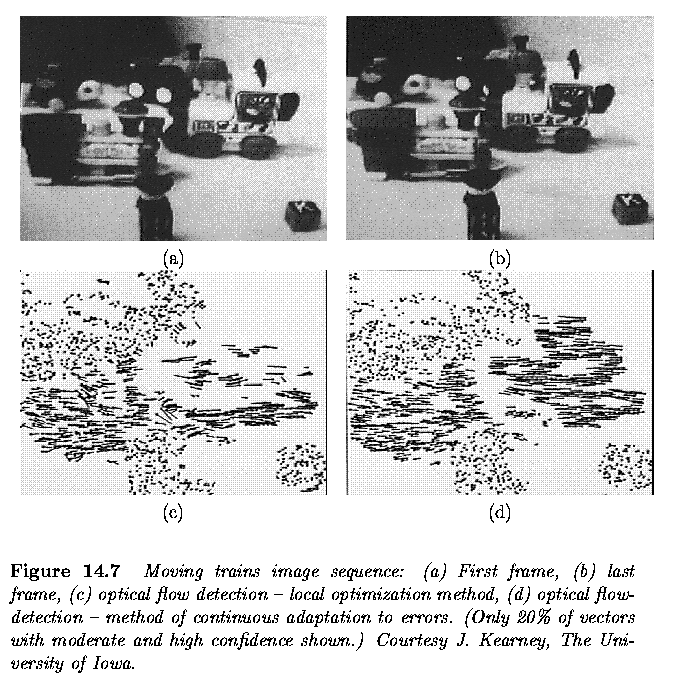
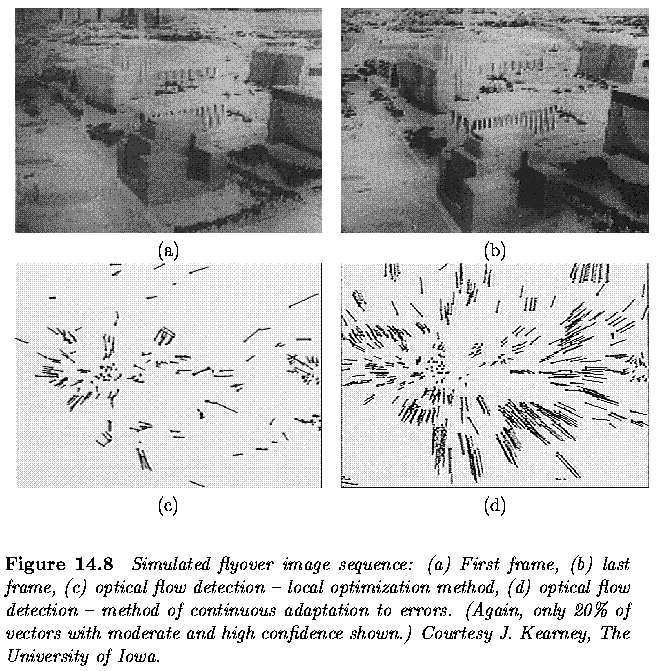
Optical flow computation approaches
Optical flow in motion analysis