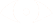Connecting to MongDB Atlas database from NodeJS (simple run directly the nodeJS file --not invoked via CGI call)
**** SEE ONLINE ATLAS FOR RECENT DOCUMENTATION ******
STEP 1: setup your MongoDB Atlas database...(see other documents for help for this) & get connection information.
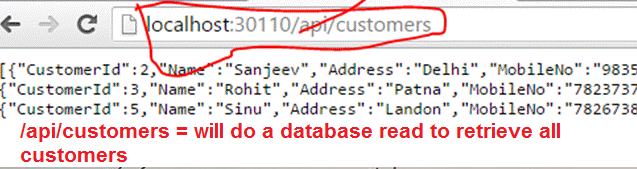
STEP 1.1: I have a database called shoppingsite with a collection call customers that I am going to access. Currently I have only 2 documents in it
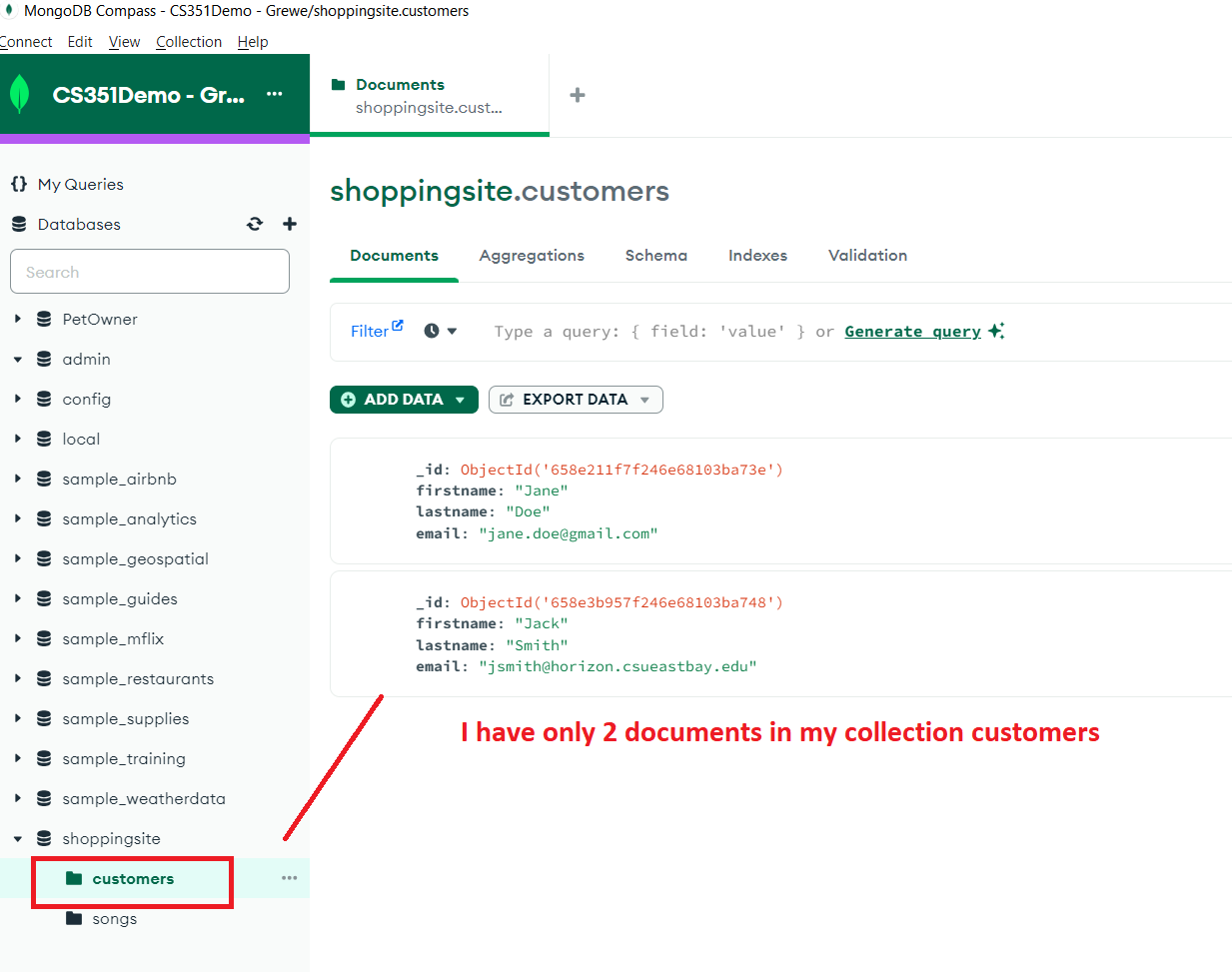
STEP 1.2: Basically you follow the directions the MongoDB Atlas console gives you when you specify you want to connect from NodeJS code in order to get the URI for connection to use in your program.
STEP 2) You will need to install the mongodb module in your project (step 2 below) by running in the terminal of your WebStorm NodeJS+Express project that you must create:
npm install mongodb
STEP 3) In your NodeJS+Express project add at the top level of the project a file called mongoDBConnectTest.js the following code
Here is the directory structure of my NodeJS + Express project with the mongoDBConnectionTest.js file at the top
Here is the code ----Read the comments to understand what it does.
const { MongoClient, ServerApiVersion } = require('mongodb'); //require model and get the MongoClient class
|
Run this FILE (not the entire project) --- here are the results
"C:\Program Files\nodejs\node.exe" C:\Users\lynne\WebstormProjects\ReadFormDataSaveMongoDB\mongoDBConnectTest.js Insert Songs into songs collection
Process finished with exit code 0 |
After running the NodeJS we get some documents in the collections songs.
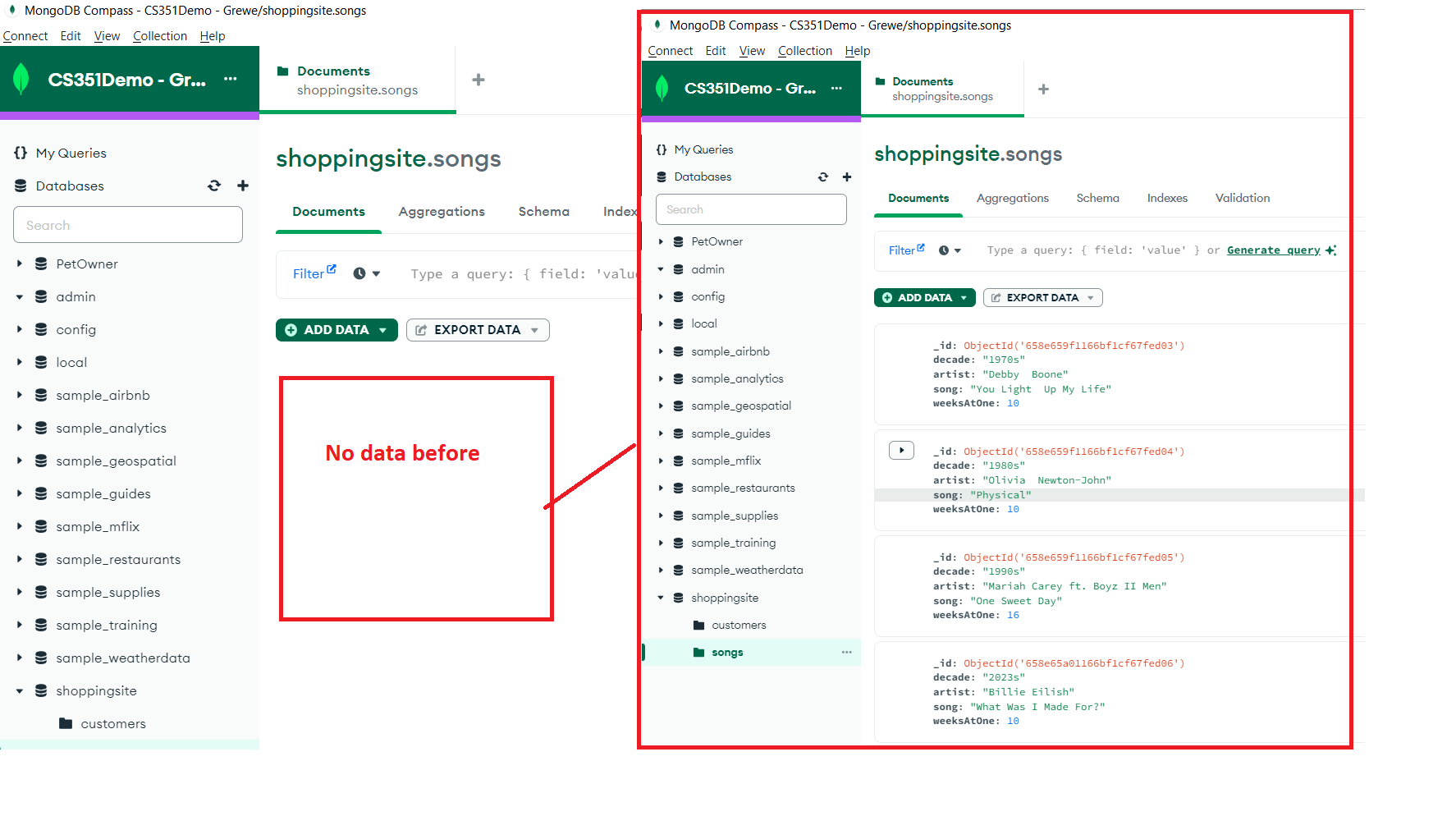
What will happen to our collection of songs if I run this NodeJS code again???
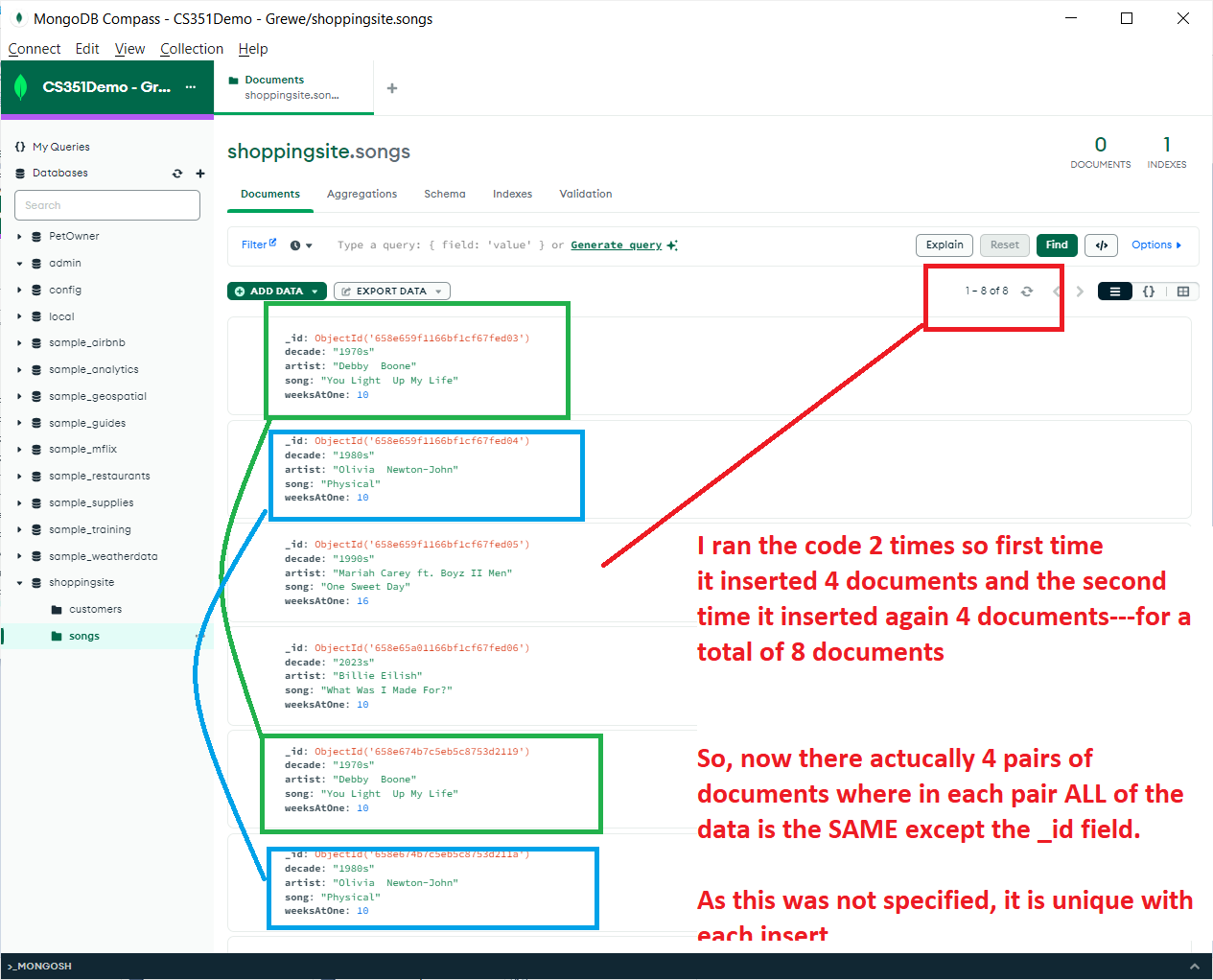
I ran the code 2 times so first time,
it inserted 4 documents and the second time it inserted again 4 documents---for a total of 8 documents
So, now there is actually 4 pairs of documents where in each pair ALL of the data is the SAME except the _id field.
As the _id (unique identifier) was not specified, it is unique with each insert --if it had been specified only 4 documents would be created regardless of the number of times I ran the code.
Understanding some of the code...more
Understanding some of the code -see CRUD (create, read, update, delete) in action
| mongodb.MongoClient.connect(uri, function(err, db) | connect to specified uri and execute function upon connection |
var seedData = [
{
decade: '1970s',
artist: 'Debby Boone',
song: 'You Light Up My Life',
weeksAtOne: 10
},
{
decade: '1980s',
artist: 'Olivia Newton-John',
song: 'Physical',
weeksAtOne: 10
},
{
decade: '1990s',
artist: 'Mariah Carey',
song: 'One Sweet Day',
weeksAtOne: 16
}
]; |
This is the JSON object representing 3 entries in our songs collection we want to enter.
NOTE: we have 4 idices (like columns) in our songs collection (like a databasetable) and they are:
|
| songs.insert(seedData, function(err, result) | try to insert new entries into the songs collection first creating the collection if it does not already exist the entries are represented by the json object "seedData" execute the function upon callback (being done) |
| songs.update( { song: 'One Sweet Day' }, { $set: { artist: 'Mariah Carey ft. Boyz II Men' } }, function (err, result) |
update entry with song='One Sweet Day' to change the artist to ='Mariah Carey ft. Boyz II Men' when done call the call back funciton specified |
songs.find({ weeksAtOne : { $gte: 10 } }).sort({ decade: 1 }).toArray(function (err, docs) { |
this is like a select (read) statment where weeksAtOne>10 and sorting by decade in asscending order (that is the :1) and then get results as an array that is passed to the call back function |
function (err, docs) {
if(err) throw err; docs.forEach(function (doc) {
console.log('In the ' + doc['decade'] + ', ' + doc['song'] + ' by ' + |
This cycles through the docs[] array representing the retrieved entries from the songs collection.
Note you access items by indexing the array docs[] with a column value called an index in mongoDB collection |
DESIGN: Direct Access from user Application or Go through an API ??????
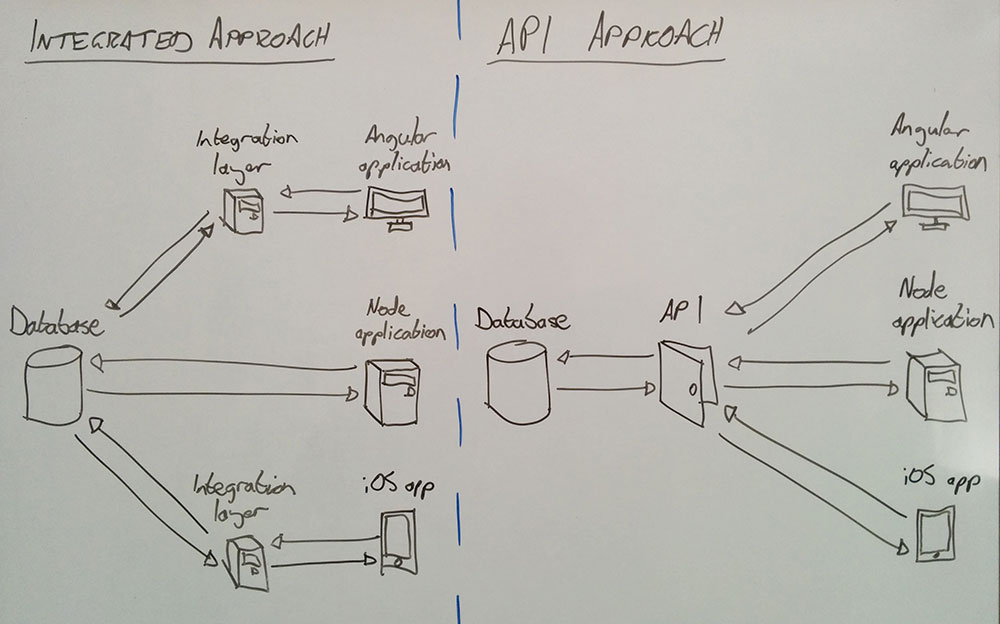
while more work creating an API initially, it means that you DONT DUPLICATE the work from your different interfaces like a web (Angular), different server application (e.g. NodeJS) or a mobile App (e.g. iOS).
What does it mean to create an API --- you create a series of spearate applications (like in NodeJS with Express) that serve up results of desired CRUD operations on your Database that are accessed via WEB URLs ---example