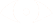Document Object Model - DOM
is the data representation of the objects that comprise the structure and content of a document on the web.
-
represents a web page as a tree of objects (accessible by JavaScript and CSS and HTML)
-
allows you to modify page elements via JavaScript after the page is loaded
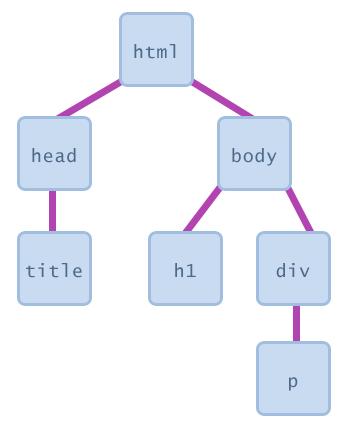
Node Object
-
The Node object is the primary data type for the entire DOM.
-
The Node object represents a single node in the document tree.
-
See w3.org for details on this object
-
Kinds of nodes include:
-
element nodes (HTML tag)
-
can have children and/or attributes
-
- text nodes (text in a block element)
-
a child within an element node
-
cannot have children or attributes
-
- attribute nodes (attribute/value pair inside the start of a tag)
-
a child within an element node
-
cannot have children or attributes
-
-
-
Properties include:
-
firstChild, lastChild : start/end of this node's list of children
-
childNodes : array of all this node's children
-
nextSibling, previousSibling : neighboring nodes that have the same parent
-
parentNode : the element that contains this node
-
DOM node object methods
- appendChild(node) : places the given node at the end of this node's child list
- insertBefore(newChild, oldChild) : places the given new node in this node's child list just before oldChild
- removeChild(node) : removes the given node from this node's child list
- replaceChild(newChild, oldChild) : replaces the given child node with the given new node
DOM creating new nodes - createElement
//create a new <h2> node
var newHeading = document.createElement("h2");
newHeading.style.color = "green";
newHeading.innerHTML = "This is a heading";
// put it onto the page in the div with id "content"
var contentArea = document.getElementById("content");
contentArea.appendChild(newHeading);
DOM accessing nodes by id or tag
document.getElementById("id")
- gets a specific element on the page
element.getElementsByTagName("tag")
- get an array of all children of the given type ("p", "div", etc.)
- can be called on the overall document or on a specific node
DOM changing associated content or attributes
element = document.getElementById("div42"); //get the element first
element.innerHTML = "This text is <i>important</i>"; // set content
element.setAttribute... //change attribute appropriately
img.src="newImage.jpg"; // where grabbed image = img here alter the source of image to new image
DOM -redirecting to a new page
window.location.href = "newPage.html";
DOM - making invisibile/visible
- Invisible:
element.style.display = "none";
- Visible:
Or, to be safe, save the original style.
element.style.display = "";
DOM objects - beyond the node object
Every Javascript program can refer to the following global objects:
- window : the browser window
- navigator : info about the web browser you're using
- screen : info about the screen area occupied by the browser
- history : list of pages the user has visited
- properties:
- methods:
- complete list
- location : URL of the current HTML page
- document : current HTML page object model