CS3340: Intro OOP and Design |
||||||
|
GIT and SW Versioning
-
GIT = is a distributed revision control system for software.
-
there are a number of free resources to use GIT and host remotely your code - GitHub and Bitbucket are popular
-
you can also buy commercial versions
-
The concept
you have code on your local development machine (local git repository) that you can create versions of and commit to a remote Git repository.
repository = a location storing and mantaining versioned code

another view
very useful --what if something is wrong in the code --you can revert (ROLLBACK) to a previous version
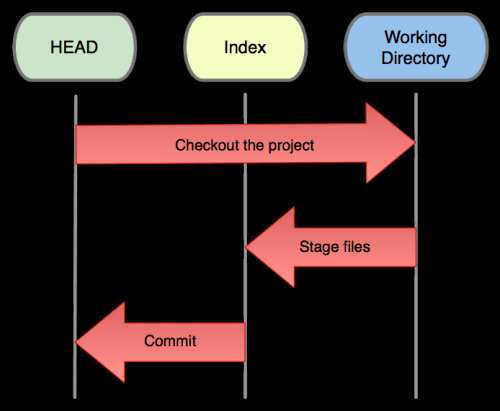
Three roles/states of GIT
The HEAD (master) |
last commit snapshot, pointer to the current branch |
|---|---|
The Index |
proposed next commit snapshot |
The Working Directory |
sandbox (local machine) |
Common operations/ nominclature
<< some operations in GIT
operations for submitting or getting code to/from repository
commit = the code is read to submit to repository
push = pushes it to remote repository
pull = gets current code from remote repository
merge = if you are trying to push code that has been pushed more recently than you pulled it by another person -- the Git system will ask you to merge the files and clean up any descrepencies. ALSO - can be used to merge branch into master.
scenario - you and Jill pull down the current code and you are both working on a file called doit.java. Jill pushes her changed code first. Then you try to push your code??? you could have changed the code in the same place --what is the system to do. You need to go through the process of merging the code and figuring out what conflicts might exist
operations for undoing/reverting to previous code
checkout = if you want to revert to a previous version BEFORE you have commited any changes
revert = if you want to undo a certain commit
Sometimes you'll want to undo a certain commit. E.g. when you notice that your changes were wrong, when you introduced a bug, or simply when the customer has decided he doesn't want this anymore
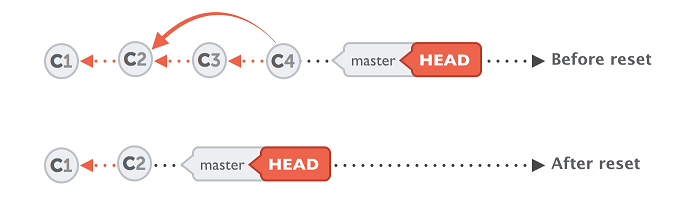
reset = if you want to go to a previous version but, not remove the commits ---basically it resets the HEAD(master) to an older branch
What we will use: BitBucket for remote GIT, eGit for support in Eclipse, local client SourceTree
https://bitbucket.org/ for details (try setting up the tutorial example and download SourceTree as part of it). SourceTree can be found directly at http://sourcetreeapp.com/
Example on How to use SourceTree with a project
Just clone your project with sourcetree on your Desktop (e.g) then add your project to Eclipse
Right click on the Package Explorer -> Import -> Project Type*** -> "Existing *** Code Into Workspace" -> Select your folder project then click Finish.
How to SETUP Bitbucket Repository and setup Eclipse with eGit (read online for more details or current interfaces) -- this shows you how to -- ONLY need to do #2 one time
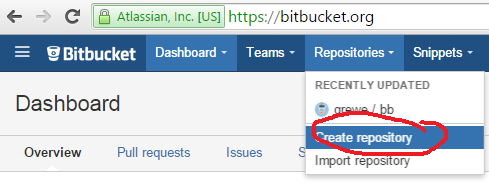
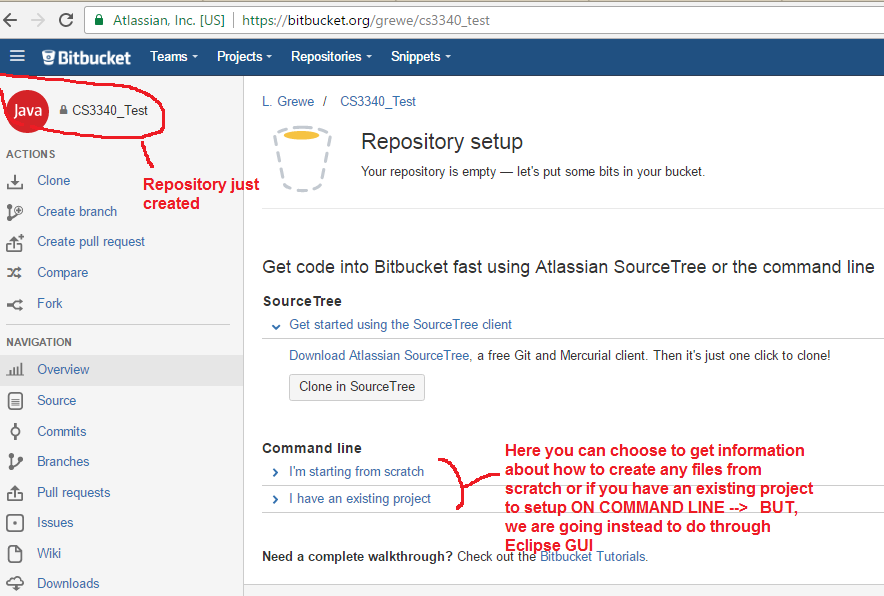
STEP 1) create a repository on Bitbucket (a git repository service at bitbucket.com)
STEP 2) (one time only)setup Eclipse with eGit (software that lets you utilize GIT)
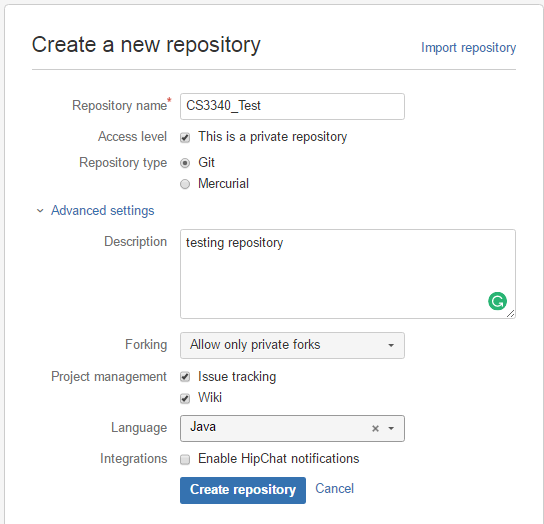
STEP 1.1: get a bitbucket account (bitbucket.org), then create a repository (Repository->Create Repository)
follow the instructions to setup a repository on bitbucket and go through initializing it as suggested
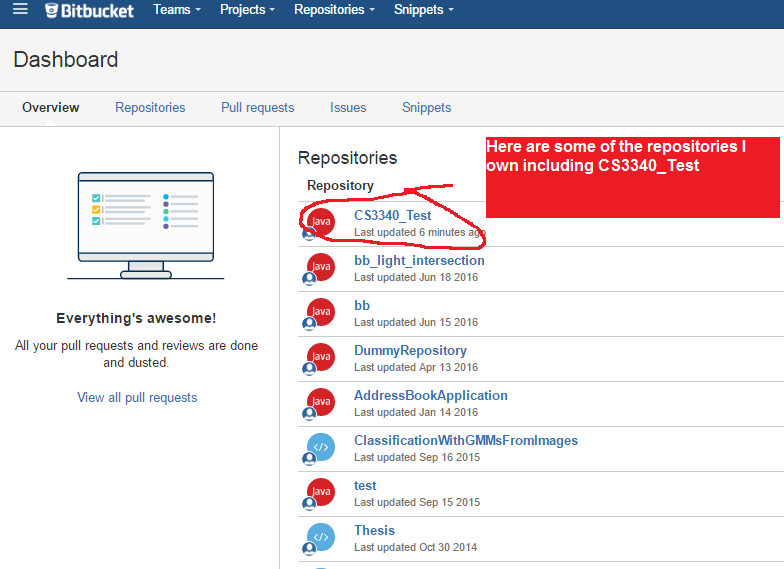
STEP 1.2: Log in -- under your overview tab you will see all repositories you are part of.
NOTE: if you hold your mouse over a repository it will tell you the URL of it (e.g. http://bitbucket.org/grewe/Tutorial)
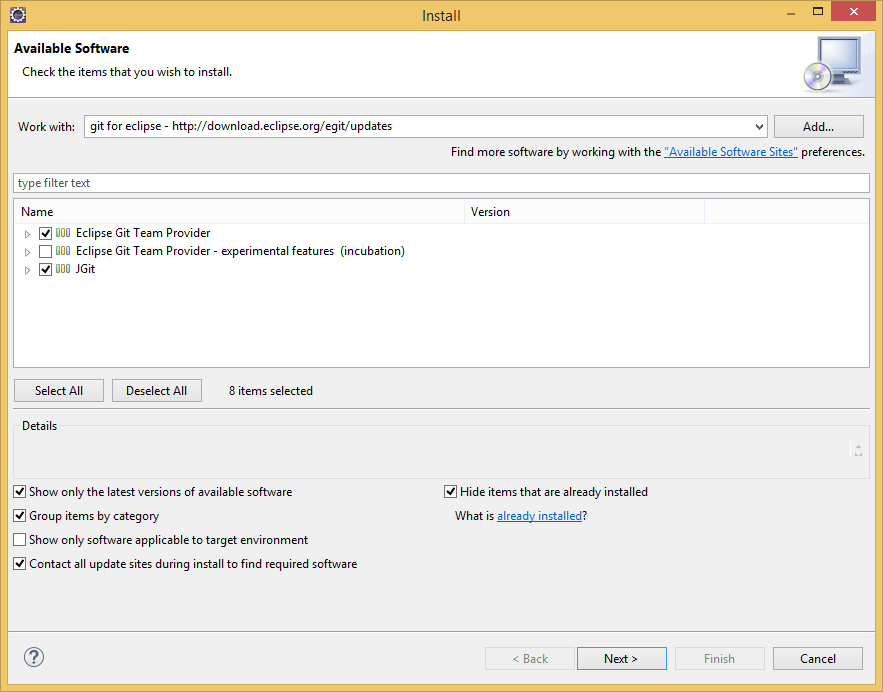
STEP 2: Launch Eclipse, then do Help->Install New Software
click the add button , the type in the url shown below
select Eclipse Git Team Provider and JGit
NOTE: when it goes to install EGit it may require you need to install other sw, just let the system do what it recomends.