|
CS1020: Introduction to Computers |
||||||
|
Human Visual System
Light is measured by frequency:Ultraviolet <---- Visible Spectrum (350-780 nanoseconds) ----> InfraRed
Light Source: Characterized by the amount of energy it emits at every wavelength.
The spectrum of a light source shows is the distribution of light energy vs. wavelength (lambda).
Perception of Light:
- Brightness. Brightness= the amplitude of the spectrum.
- Hue. Informally refered to as color.
- frequency componets of spectrum
- characterized by dominant frequency
- wavelength DOES NOT equal hue.
- Saturation. Spectral width, describes "whiteness" of a color
- unsaturated = a lot of white
- saturated = no white
- Emitted Light
- Reflected Light
The Human Eye
Three levels of membranes.
Outer = Cornea: Transparent area, and Sclera: Opaque
Choroid:
- network of blood vessels
- heavily pigmented
- ciliary muscle: allows focusiing of the lens
- iris: like a diapragm, controls quantity of light
- made of layers of tissue
- 60 -70% water
- slightly yellow
- absorbs 8% of visible light
- contains photorecptors, sensors that detect light
- contains rods and cones
- rods:
- 120 million, several per nerve ending
- achromatic vision = b/w, grayscale
- work well in low light conditions
- low spatial detail
- related to peripheral vision
- cones
- 6-7 million
- fovea
- color
- fine detail
- work well in bright light
- 3 types, r, g, b
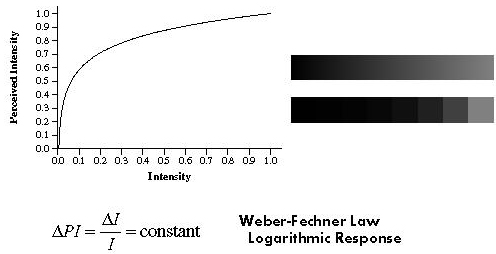
- Our perception to brightness